GAF QuickMeasure
GAF QuickMeasure
Reports
Within a GAF QuickMeasure report, you’ll find precise roof dimensions and structural details, including total square footage, pitch, ridge length, valleys, eaves, and other key measurements. The report often includes recommended materials, helping you estimate the required quantity of shingles, underlayment, and accessories. Ultimately, this data provides a clear, comprehensive snapshot that enables accurate pricing, efficient planning, and better communication with both team members and customers.
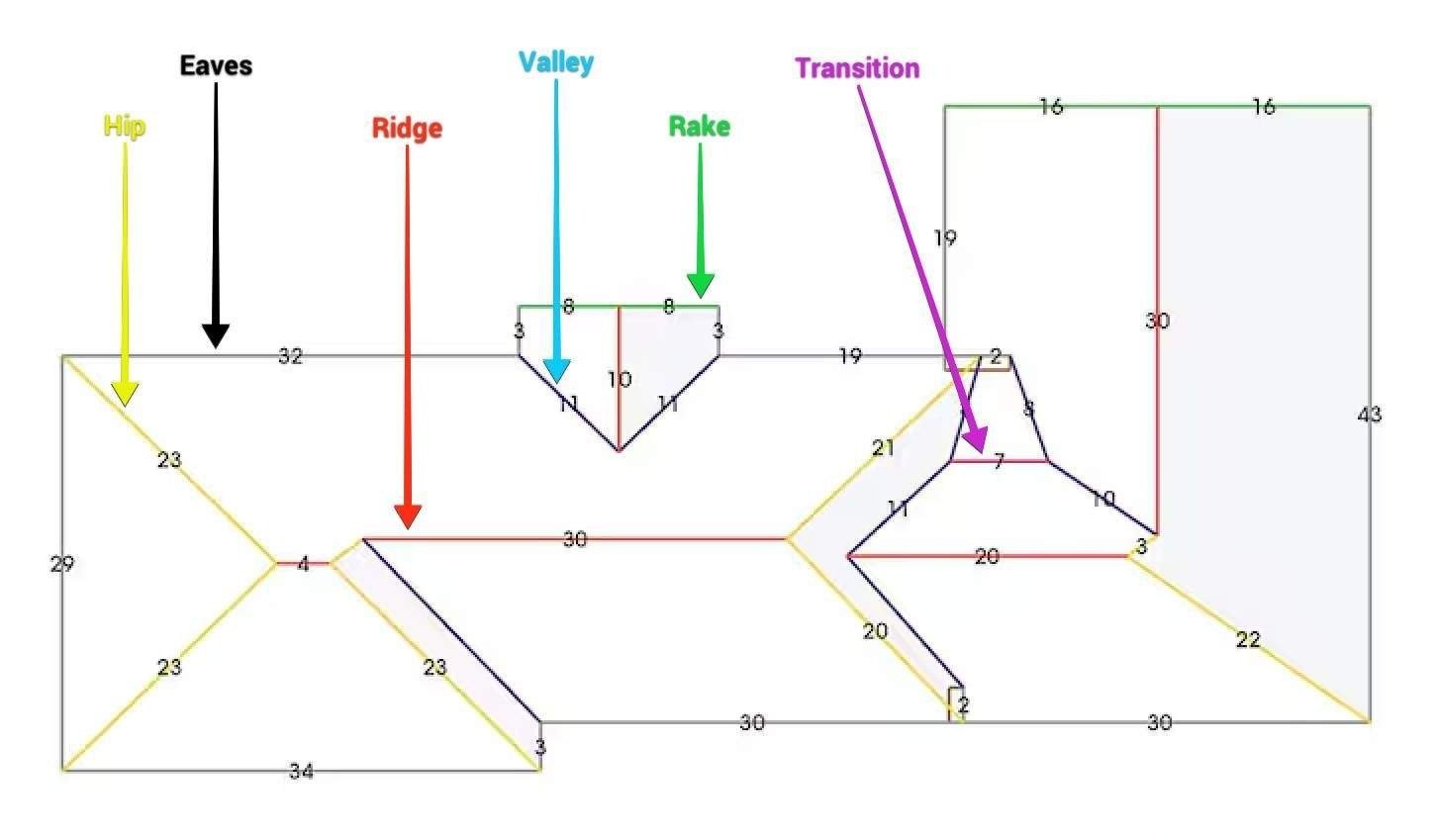
Eave: The edge of a roof that extends beyond the exterior walls of a building, providing shade and protecting the walls from water runoff.
Hip: The external angle formed where two sloping roof planes meet, typically running diagonally from the ridge to the eave.
Rake: The sloped edge of a roof that runs from the eave to the ridge on a gable end, often extending beyond the wall for aesthetic and protective purposes.
Ridge: The highest horizontal line on a roof where two sloping roof planes meet, often capped to prevent water infiltration.
Transition: The area where two different roof sections or materials meet, such as where a steep slope connects to a flat surface or a new addition joins the existing roof.
Valley: The internal angle formed where two sloping roof planes meet, creating a trough that channels water runoff to the gutters.
Roof Pitch: The measure of a roof’s steepness, expressed as a ratio of the vertical rise to the horizontal span (e.g., 6:12 means 6 inches of rise for every 12 inches of horizontal run).
Flashing: Roof flashing is a thin, weather-resistant material (commonly metal) installed at joints, edges, or transitions on a roof to direct water away from critical areas, preventing leaks. It is used around chimneys, skylights, vents, and where the roof meets vertical surfaces like walls.
Step Flashing: Step flashing is a type of roof flashing designed for sloped roofs, installed in a stepped pattern where the roof intersects a vertical wall. It is layered with shingles to create a watertight seal, directing water away from the roof and preventing leaks.
Notes:
Roof Pitch - 0:12 to a 2:12 is considered a flat roof. 3:12 and above is a sloped roof.
The eave detail number included both the flat eave and the sloped eave. They need to be separated correctly.
Flat roof area always has a 15% waste factor.
Example: 1000sq x 1.15 = 1,150sq \ 100 = 11.50 = 12 SQ
Please schedule a one-on-one with me when the time works for you.